Autodesk Inventor 2025
2025 marks 25 years of Autodesk Inventor! A quarter of a century dedicated to designing and making your best products. This webinar hosted by Autodesk’s Product Marketing Manager, Jim Byrne, and KETIV’s Senior Technical Solutions Executive, Thomas Fitzgerald covers the 2025 updates to Autodesk Inventor.
This update brings over 142 enhancements, each carefully crafted to improve user experience, enhance functionality, and streamline design processes. Watch the webinar as the team of experts cover:
- Part Modeling
- Sheet Metal
- Assembly Modeling
- Drawings
- Interoperability
This release of Inventor brings a series of features and functionalities that streamline your design process, improve your user experience, and promote interoperability, ensuring that you’re equipped with the most advanced tools that work exactly how you expect them to.
Autodesk Inventor 2024
Inventor 2024 is packed with new features and enhancements to improve your design experience. You will find enhancements for 3D annotations as well as 2D drawings and notice the new performance and time-saving enhancements in this update.
In this webinar, KETIV Application Engineers cover general enhancements, part modeling enhancements, 3D annotation enhancements, and more updates in Inventor 2024!
Autodesk Inventor 2023
Autodesk Inventor 2023 is packed with customer-requested improvements and enhancements, so you can focus more on design and innovation—and less on repetitive tasks.
Watch this KETIV Virtual Academy with Autodesk team members, Jim Byrne and Luke Mihelcic as they cover:
- Performance improvements to work faster on large and complex assemblies
- Interoperability enhancements to make sharing your designs easier than ever
- And part modeling upgrades to help better prepare your designs for manufacturing
Learn how the updates in Inventor 2023 deliver and improve on the professional-grade tools you depend on every day.
Autodesk Inventor 2022
It is that time of year, when everything blooms, kids go crazy at spring break and Autodesk unveils the newest and most exciting product features. The Autodesk Inventor 2022 release is designed to give end users more productivity as well as a more reliable workflow with fewer steps.
Autodesk is listening to you through interactive sessions, Inventor Ideas Station, Beta Tests and Feedback Communities. Parts, assemblies, and drawings have all been enhanced in response to user requests. Here is a list of the highlights in this
Inventor 2022 release.
- Model States are here!
- Instance Properties provide unique reference for components
- Fillet command is now in the Properties panel further streamlining usage
- Performance improvements
- Better workflows from Inventor to REVIT and Fusion
- Fusion Team collaboration tool is now included in the Product Design and Manufacturing Collectionand Fusion 360!
- iLogic additions to address new features
Let us take a closer look at all that this new Inventor has to offer.
What’s New in Inventor 2022
Productivity
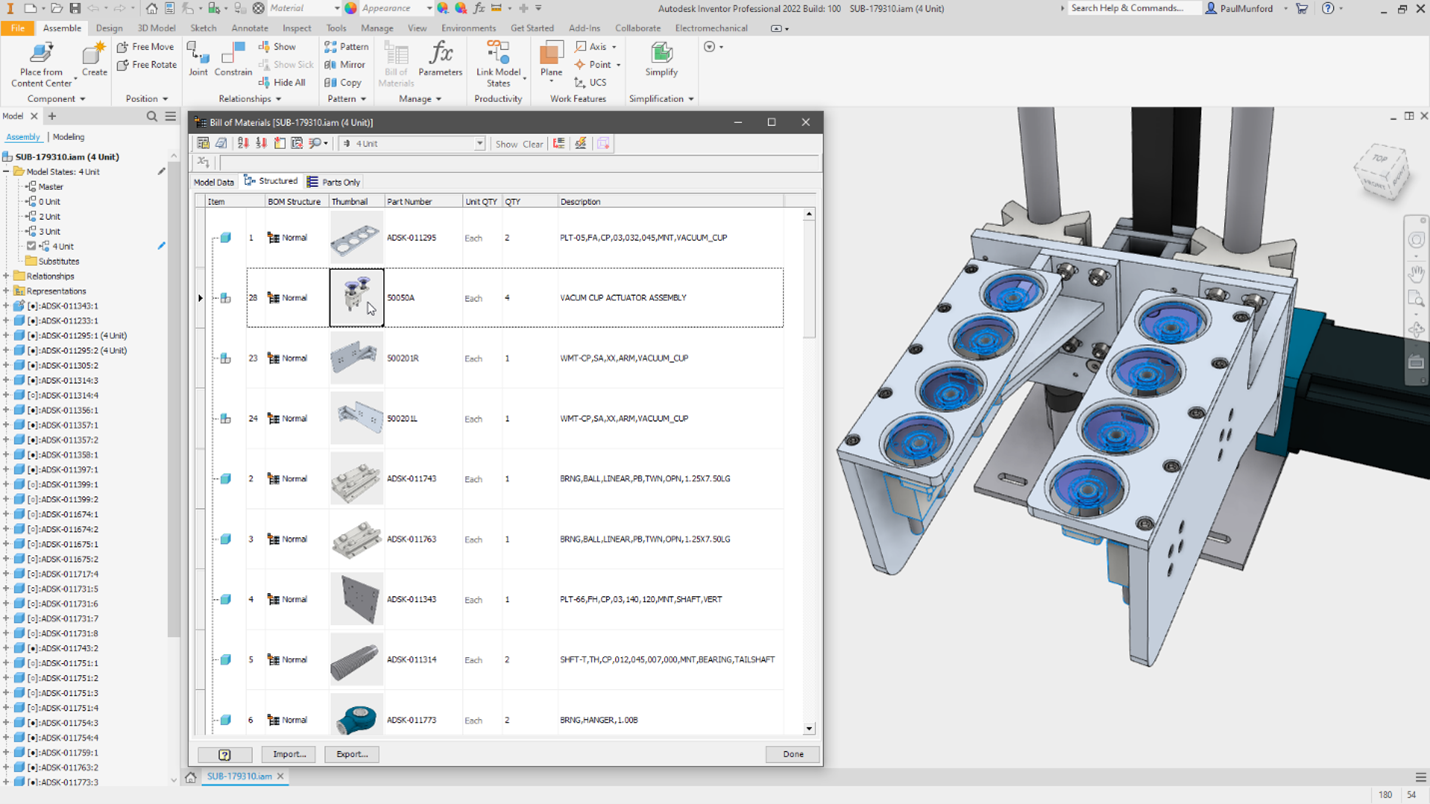
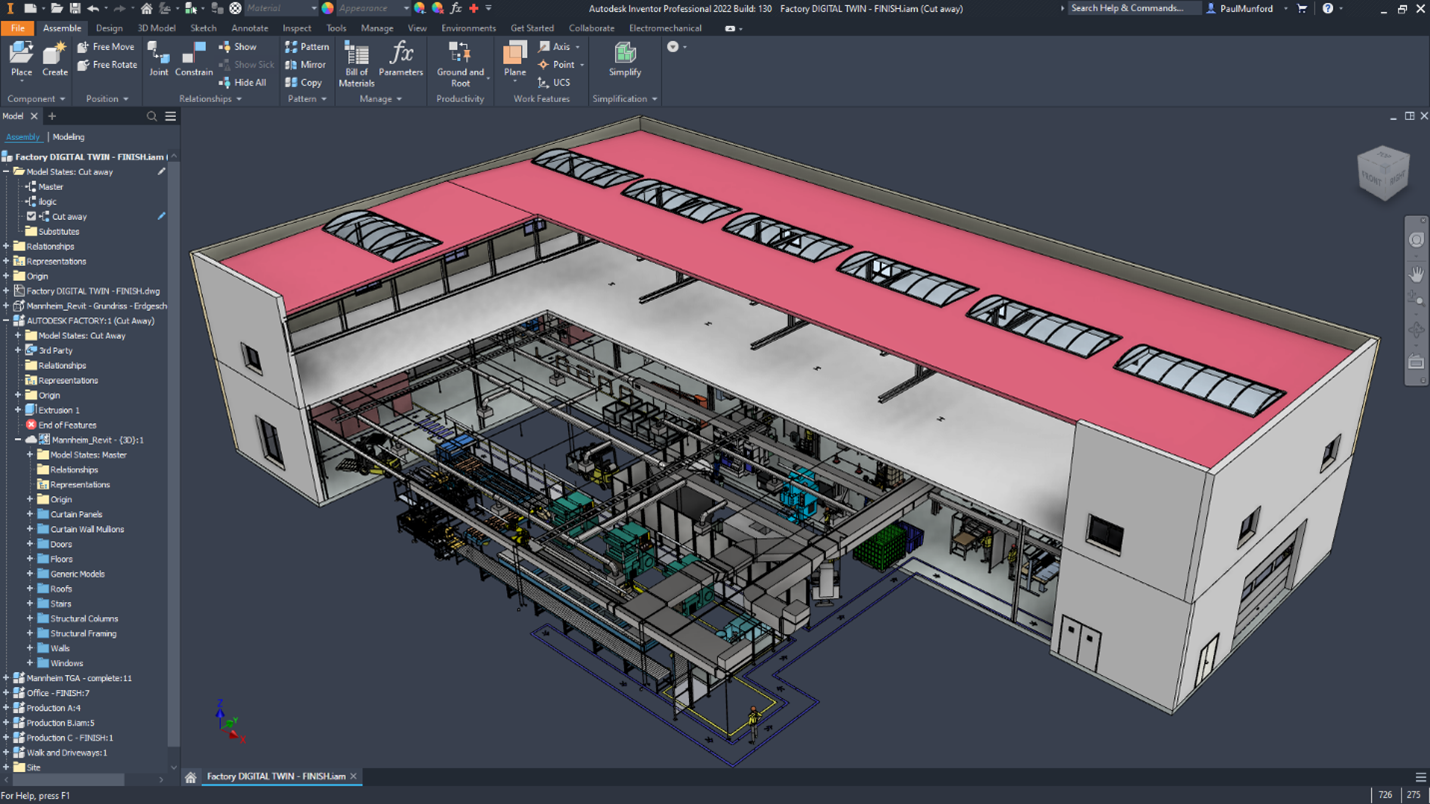
Model States is one of most long-awaited features of What’s New in Inventor 2022. Model States enables you to create multiple representations of a part or assembly contained in a single model, to provide a convenient way to engineer, manage, and manufacture your designs. Just a few of the more requested use cases are for assembly positions, tooling machining operations, multiple fold operations for sheet metal, bill of materials and more.
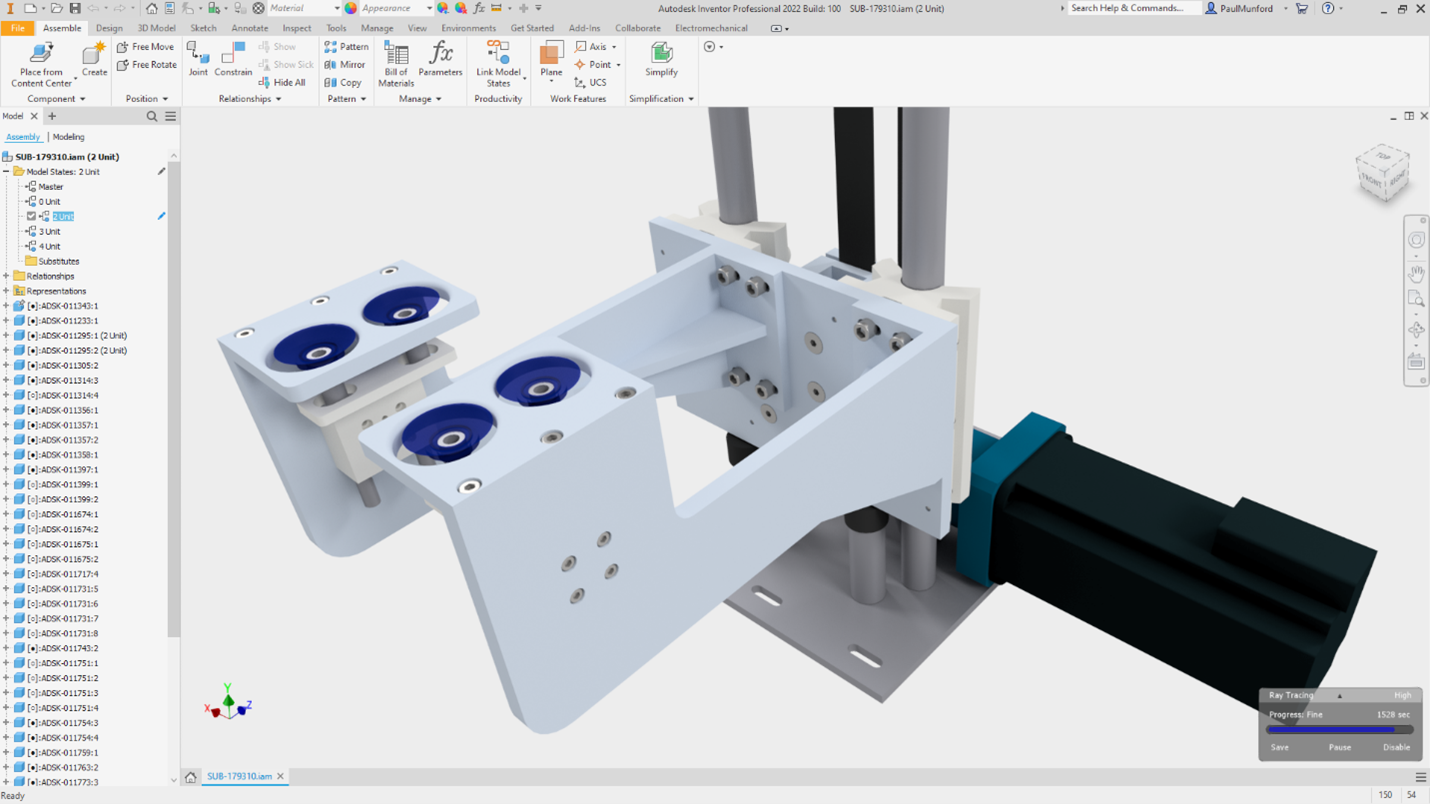
Instance Properties is a feature that many customers have requested. This ability enables you to assign unique properties to duplicate components within an assembly document. Assigned properties are stored in the assembly file so they will not affect the original referenced component. They are available for display in balloons, leader notes, and parts lists. Think unique ID, or reference designator!
New options for under constrained components, allow you to constrain your models in your assembly without a time-consuming process.
The simplify command has been enhanced to remove complexity and your intellectual property from your design before sharing with those outside of your organization. The new simplify command is now on the property panel for a more efficient workflow. Presets have also been made available to save settings for future simplification projects.
The fillet command is now in the property panel and divided into three categories Fillet, Face Fillet, and Full Round Fillet. This will simplify the number of fillet options in the property panel for a straightforward and efficient experience.
Drawings now include shaded drawing views now can reflect the lighting styles, camera views and 3d annotations.
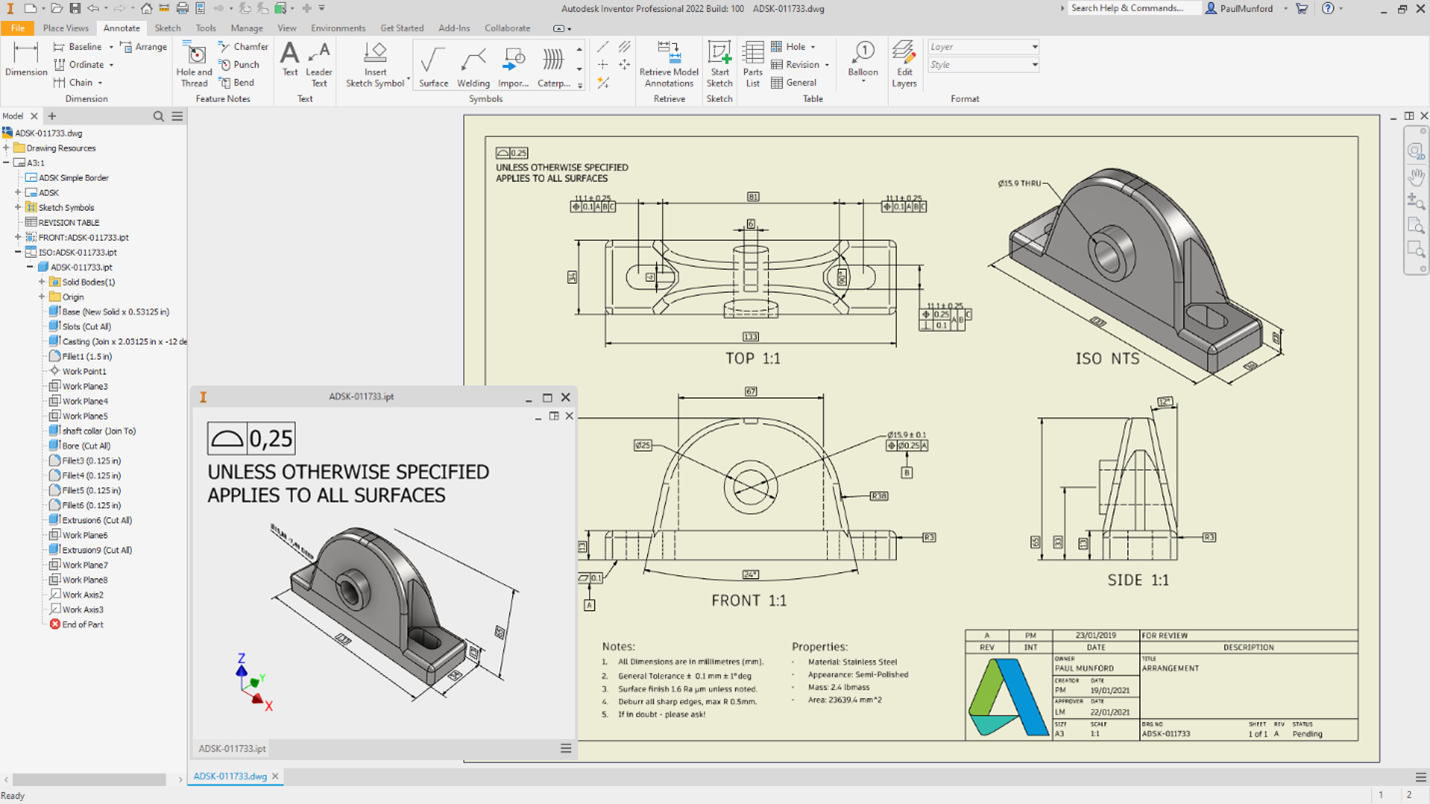
Additionally, you can now export to QIF (Quality Information Framework) 3.0 is now supported to include PMI (Product Manufacturing Information) data. QIF is built on the XML framework for easy integration and interoperability with other systems.
Experience Improvements
We are all loving the new installer interface and online deployment builder which is much easier to navigate and more intuitive so you can get your team up and running on the latest release in less time.
The Property Panel continues to see enhancements that improve efficiency, including new keyboard shortcuts and color validation to highlight input errors.
Defining the precise location and function of your assembly design is essential to successful production. New symbols in the assembly browser help identify parts that may need additional constraints to fully define them.
The dark theme user interface been so successful it has been promoted! It is now available across the Inventor application so users can enjoy an experience that reduces eye strain.
Performance
One key performance update is Faster Application Startup gets you to designing sooner!
In-place edit performance has been improved for sketches, features, and object visibility settings.
Graphics Display has been enhanced by changing view orientation, panning, and zooming in and out. Edge silhouettes are rendered using the GPU, and improving the performance when using those visual styles with edge silhouettes. Additional improvements are Wireframe Visual Styles and in-place editing for part assembly and sketch environments.
Connected Workflows
Export to Revit incorporates the new Simplify command to produce a REVIT model containing only the components and features needed for the Revit design. The Revit Export and Simplify commands have been combined and added to the property panel for a complete set of options in one easy-to-use interface.
Interoperability between Inventor and Fusion 360 enables engineering workflows including Generative Design, electronics, manufacturing tools, and consumer product design. A new command is added to the Environments tab that allows you to bypass Desktop Connector and send your part file directly to the Fusion Team.
Did you know that Fusion Team is now included with a subscription to Fusion 360 and the Product Design & Manufacturing Collection?
Automation
iLogic which allows for automation in Inventor has been expanded to support the new Model States and instance properties.
As you can see, some great features have been added to Inventor 2022. Sign up for KETIV’s weekly webinar, KETIV Virtual Academy, where you can see these new features in action in our What’s New in Autodesk Inventor, AutoCAD, and Vault 2022!
Autodesk Inventor 2021
It’s that time of the year once again when Autodesk introduces its latest and greatest version of Inventor. Below is What’s New in Inventor 2021.
The Inventor 2021 release is structured around greater productivity for the end user as well as a more efficient workflow with less of headaches. Also, for everyone who has posted about changes and requests for the following updates of Inventor using either the Inventor Ideas or Feedback Community, Autodesk is listening! Autodesk has made improvements to parts, assemblies, and drawings based on what users are asking for. This is everything that Inventor 2021 flaunts:
- Performance, Productivity, and Experience Improvements
- Assembly Enhancements
- Frame Generator
- Tube and Pipe
- Connected Workflows with Revit
- Parts-Level Improvements
- Automating Drawing Creation
Let’s go ahead and take a deeper dive into everything this new Inventor has to offer.
Learn more about Autodesk Inventor 2021.
Performance, Productivity, and Experience Improvements in Autodesk Inventor 2021
Every year Inventor offers a performance improvement to accommodate the needs of users at all skill levels. They have addressed the following areas in the most recent release to mitigate performance issues and improve stability:
- Improved performance when selecting multiple components
- Improved performance when inserting sub-assemblies
- Select or Saved Views makes visibility status changes faster
In terms of productivity, users will see that property panels have expanded into key features used regularly. The property panel workflow is now included in Bend, Coil, Combine, Copy Object, Decal, Delete, Face, Split, Thicken/Offset, and all Frame Generator commands. Moreover, more access to properties will streamline user workflow.
For Inventor experience, in our blog What’s New in Inventor 2020, they released a brand-new Light Theme user interface. In the Inventor 2021 version, the next best thing to a Light Theme is the Dark Theme counterpart. Therefore, Inventor 2021 can now match dark theme mode on browsers or apps like Google, Reddit, and Instagram.
Assembly Enhancements
Two big assembly enhancements in Autodesk Inventor 2021 include Frame Generator as Tube and Pipe. Both features have a numerous amount of productivity enhancements that allow the end user a more pleasurable experience:
Frame Generator
- Improvements to the file naming dialog allow for more concise controls of naming schemes for frame generator components. What’s more, there is a new option that allows the file name of the component to be like the one on the browser.
- Creating frames is more streamlined and more efficient with the new Category features. They allow the user to make frame selection easier. Besides, a new Preset allows users to save their commonly used frame settings for future use.
- You can now control filtering geometry from the property panel. There is also a new preview glyph which aids in orienting the frames as the skeleton geometry is selected.
- The introduction of a new zooming tools allows the user to adjust the view. Therefore, it makes it perpendicular to the frame manipulator or to a zoomed-in isometric view of the frame manipulator. When finished, the user can zoom back to the initial view.
- Trim/Extend command will now terminate the member on a curved face.
- Two new notch profiles are added to end treatment, extending notch support “I”, “C” and “T” profiles. Circular members will have the same feature as well.
- Autodesk has reworked the Reuse command. It is now easier to select the original member in a collection of frame members to be reused and populate it to a skeleton geometry.
- You can also now choose the Unwrap command to be aligned with the model or any of the default planes. Multiple planar holes can now be selected to be Rigid.
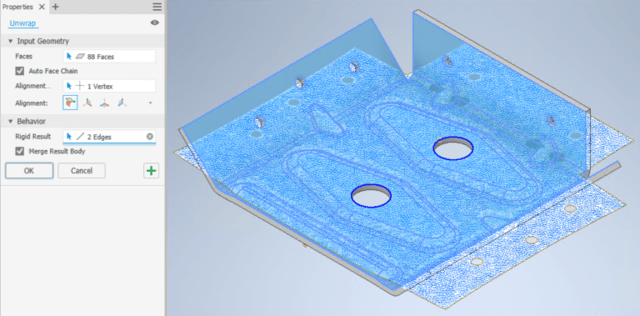
Tube and Pipe in Autodesk Inventor 2021
- Autodesk has extended File Naming dialog to the Mirror and Copy commands.
- A new option when saving files allows the user to set default behavior whether to save the files or not. A new column called “Saved State” in the save dialog will tell what files Inventor is prompting the user to save and why.
- Shaft component generator will have extended functionality to bolted connection, allowing it to help structure assemblies. Once active, it won’t create a folder or subassembly on disk and directly places the individual components into the assembly. Doing this will open more options for structuring the assembly and organizing the date.
- File naming for Tube and Pipe designs continues to be improved. (Not available for Inventor LT)
- When creating multiple route, the Appy button with Auto-Route options keeps users in the command to create the next route.
It is important to note that some of these new updates will not be seen in the latest release of Inventor LT.
Connected Workflow with Revit
Many architecture and engineering companies would love to see improvements to the Revit-to-Inventor workflow. What’s New in Inventor 2021 now includes AnyCAD functionality for Revit. It allows manufacturers in the construction industry to better collaborate on BIM projects. Specifically, here is how the connection from Revit to Inventor has been changed or improved:
- The interoperability between Revit and Inventor has been enhanced by keeping an associative link between the inserted Revit data. The Revit project is accessible from either a local file or from the cloud using the Autodesk BIM 360 common data.
- Changes to the Revit model will be automatically updated within the Inventor assembly. Without File Translation, any changes to the Revit project will therefore update the Inventor assembly.
- JT exports can now support the export of software-interpretable, semantic Product Manufacturing Information (PMI). It is much better because prior to this, the PMI box exported graphical data.
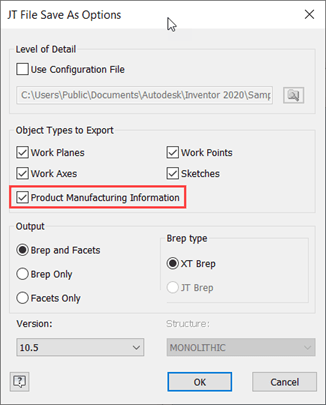
- Parasolid version 32 import is now supported
- AnyCAD and the Import formats are now updated for Solid Edge. SolidWorks, and Unigraphics.
Part Level Enhancements in Autodesk Inventor 2021
Another part of Inventor that users were looking for improvements is within the part level. In fact, the three areas where Inventor 2021 is enhanced are sheet metal, multi-body parts, and 3D Annotations. They are as below:
- Sheet metal flange can now be defined by a reference plane or face which makes it easier to match precise angles.
- Mouse clicks have been significantly reduced by using the familiar window selection. This allows users to select multiple bodies or faces in the part.
- There is now a consistency between the Custom iProperties and 3D annotations by referencing each other into leader notes and general annotations.
Drawing Level Enhancement
Autodesk Inventor 2021 delivers drawing-level enhancements by automating documentation tools. This will allow the users to streamline their workflows.
- Line Style has changed to Display Style. This now offers more options for finer control of the appearance of BOM Reference parts in a drawing.
- Automated centerlines can be added to drawing views and are easier shown with their own dedicated button click in the ribbon.
- Inventor can now easily detect diameter dimension for side views or section views when selecting parallel geometry.
- One of the most popular requests was to return the Measure command back to the Tools tab in the drawing environments. This allows for the user to take measurements without adding additional annotations.
- A brand-new option, “Rotate” in the Dimension command, allows user to align a dimension perpendicular to a selected edge.
- Copying and pasting general tables in a drawing sheet has been streamlined in order to speed up the completion of documentation.
- If the view layout is saved as a sheet format, it will now retain view settings. There is also a new option to “Fit views to sheet” which will automatically scale the view.
- Sheet formats will now support flat patterns for sheet metal parts. Parts list for assemblies are all automatically populated from the referenced model during sheet creation
- Autodesk has improved iLogic to help users add dimensions, notes, and balloons from labeled features.
- Drawing styles can be changed with the support of iLogic. This will make it easier to change styles based on the customer, or it can help batch edit styles to aid CAD standard compliance.
In conclusion
Autodesk has made a myriad of improvements in Inventor 2021. These are all the highlights for What’s New in Inventor 2021.
Watch the Virtual Academy session on Inventor 2021 below:
To keep up with all changes in the latest releases, sign up for KETIV’s weekly live online training, KETIV Virtual Academy.
Autodesk Inventor 2020
Autodesk is constantly working to gather customer data to drive yearly improvements to their products. In fact, customer-driven improvements from the Autodesk Knowledge Network and Autodesk forums have helped to drive some exciting changes for “What’s new in Inventor 2020”. Keep reading to learn about the top 4 updates.
What’s new in Inventor 2020?
1. Design Enhancements
Some of the main design enhancements within the Sheet Metal part environment include more options for identifying and selecting sketch geometry. An example is closed loops. In addition, sketch blocks now display in relation to their consumed features.
One of the most existing changes is the ability to create flat shapes with the brand-new unwrap command. Furthermore, even more complex geometries wouldn’t be a problem! You can also flatten shapes that could not be previously flattened within the Sheet Metal environment using this command. As a result, this command has options for specifying sides to remain straight or holes to remain circular. This expands the ability to create sheet metal designs for more complex designs.
2. Inventor User Experience
Another key update is the fresh new look for the Inventor 2020 user interface. This includes new property panels with the aim of helping to reduce picks and clicks.
What’s more, some newly added property panels include the extrude, revolve, sweep, and thread commands. These would aim at increasing productivity and flexibility within these commands.
3. Frame Generator Enhancements
Many of the frame generator enhancements came from user-requested updates including updates to in-canvas manipulations. These allow you to place, offset, and rotate selection and make it easier to visualize the orientation of frame members.
Updates to the notch command to include custom profiles and trim command allow for even greater flexibility within your Inventor Model. In addition, they have added custom endcap families to the content center library to increase future design efficiency.
4. Translation and interoperability
Like Inventor 2019, Autodesk is always working to improve integration with non-native CAD data. Inventor 2020 continues to work with tools like Solidworks and has expanded translation connections. Therefore, it allows users to leverage CAD files from many different sources.
In addition, Autodesk has made it easier to connect with Fusion 360 to bring your Autodesk Generative Design workflows into inventor 2020. Users can now reference Fusion 360 files within Inventor, eliminating the need for import/export. This means a change you make within a Fusion 360 model will automatically update everywhere you reference. Hence, it will be saving time and creating a more seamless workflow.
Check out more Autodesk 2020 updates here!
Take a look at the full Virtual Academy video on Inventor 2020!
Autodesk Inventor Nastran 2020
What’s new in Inventor Nastran 2020?
The newest release of Autodesk’s flagship finite element analysis software, Inventor Nastran 2020, sees some major changes compared to previous versions. From an improved user interface to automated mesh refinement to easy file management, Inventor Nastran 2020 is designed to provide a seamless CAD-CAE-data management workflow.
New Name, Fresh Look
The most fundamental change to this year’s release is the name – Nastran In-CAD is now Inventor Nastran. Users will also notice a new, cleaner look to the Nastran environment in Inventor. The expanded Constraints section provides easy and direct access to the Frictionless and Pin constraint types.
Inventor Nastran 2020 uses and displays the same unit system throughout the model as tgat ub in previous versions, where the ribbon and Model Tree units were not always the same as the unit system we use for the analysis. Material tables now have more relevant labels, and the new release works smoothly with Frame Generator models.
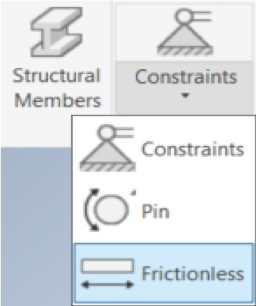
Hydrostatic Load
The 2020 release has a new load type – hydrostatic load. This enables the user to analyze the hydrostatic pressure with respect to the depth of a fluid in a specific direction. The hydrostatic load offers a much simpler definition than the variable pressure load in past releases.
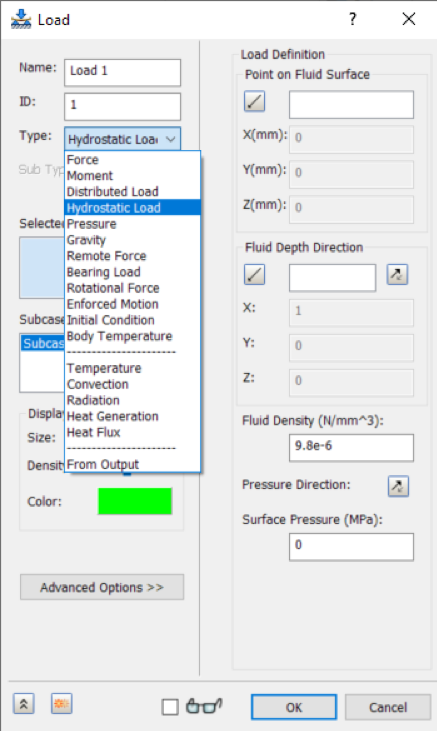
Mesh Convergence
With Inventor Nastran 2020, obtaining a mesh independent solution is simple and automated. The Mesh Convergence dialog lets users specify the number of refinements, refinement criteria, and the option to refine the mesh either locally or globally. This new feature helps ensure the accuracy of the FEA solution with respect to the mesh.

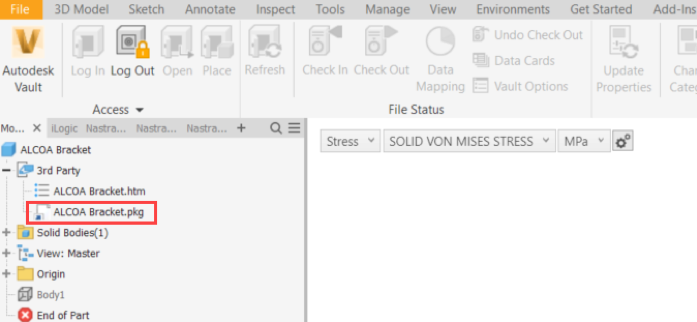
Manage FEA Files with Vault
With Inventor Nastran 2020, you can store and manage the FEA files generated by using Autodesk Vault. Then, you can store Inventor Nastran results in a single PKG file, which appears in the Inventor Model Tree. The Vault PKG file can also be easily updated to reflect any changes made in the model.
If you’d like to learn more about the 2020 updates, check out more resources here!
You can also view the Virtual Academy video below!
Autodesk Inventor 2019
Autodesk Inventor 2019 delivers user-requested enhancements and continues to provide the professional-grade 3D mechanical design and engineering tools you rely on.
Check out this video that gives an overview of the 2019 updates to Inventor, and be sure to check out our YouTube channel for a deep dive into all the features.
Autodesk Inventor 2018

The wait is over! Autodesk Inventor 2018 is now available to download and here’s your first look at what’s new. This year, Product Managers at Autodesk have focused much of their efforts on adding professional-grade design enhancements, an expansion to interoperability, and improvements to the user-experience.
Read about it below or watch as Autodesk Product Manager, Loren Welch, gives a guided tour of the new features and updates in Inventor 2018.
Professional-Grade Design
Autodesk Inventor Product Managers have spent a lot of time improving the entire design workflow. My particular favorite enhancement is the addition of Model Based Definition (MBD) and 3D Annotations.
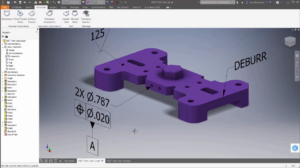
Inventor now has integrated GD&T and 3DA so that users can finally include important information in the 3D model space and accelerate traditional 2D drawing production. The best part about it is the fact that Inventor automatically recognizes tolerance features such as holes, and will use the correct GD&T symbol for that particular definition.
Expanded Interoperability
Autodesk has made the difficulty of working with foreign CAD files a thing of the past. AnyCAD was released in Inventor 2016, and has seen improvements in both of the last two major releases. Inventor 2018 brings in one of the most requested improvements to that workflow – backwards compatibility. You can now work between 2017 & 2018 seamlessly, whereas before your entire team would need to be on the same version of the software to collaborate. This allows early adopters to take advantage of the newest features, while some can remain in the previous release if needed.
In addition to AnyCAD improvements, the Inventor team also included enhancements to the Shrinkwrap functionality, specifically improving the flow of BIM content from Inventor, as well as the ability to more easily incorporate DWG underlays into your 3D workflow.
Enhanced Inventor Experience
The overall user experience has been enhanced for greater productivity and flexibility per feedback from users like yourself from around the world. As a member of the Inventor Beta community, I have seen a lot of these features grow from their infancy. The measure tool has seen some redesigning and the browser has some great features such as improved search functionality that can tell you immediately if files are unresolved or out-of-date.
The Product Managers included over 50 user-requested ideas into this release of Autodesk Inventor 2018, and they are always looking for new suggestions to fuel upcoming releases. Check out the Inventor Idea Station to make your voice heard.
Join the KETIV Virtual Academy and never stop learning new features introduced to the tools you use most.
Part 1: AnyCAD and Backwards Compatibility
This is the first part of What’s New in Autodesk Inventor 2018. We will cover the new features of this release: AnyCAD and Backwards Compatibility. Let’s get started.

AnyCAD and Backwards Compatibility
What is it? Autodesk has continued to take steps in improving the AnyCAD functionality in Inventor. This release contains what may be the largest enhancements ever since AnyCAD’s inception. Users can now use AnyCAD workflows to leverage Autodesk Inventor 2018 parts and assemblies into Inventor 2017 designs.

Why I’m excited. This is groundbreaking. One of the most requested enhancements to Inventor has always been backwards compatibility. Users have had to maintain a singular version among themselves and their contractors, vendors, etc. in order to collaborate on a project. If one person opened your assembly in a newer version, the file was stuck there.
You can now take Autodesk Inventor 2018 files and open them in the 2017 version of the software. This is great for supplier and vendor collaboration, especially if you want to be an early adopter of the latest version of Inventor. This, in addition to the already existing workflow for non-native files, lets you work in a mixed CAD environment and maintain the most updated versions, allowing you to get your designs to production at a faster rate.
Data collaboration struggles are common, and hopefully you too can use AnyCAD technology inside of Inventor 2018 to eliminate some of the speed bumps in your design process.
Now, let’s take a quick look at new Autodesk Inventor 2018 feature, AnyCAD, in action:
Join the Autodesk Virtual Academy and never stop learning new features introduced to the tools you use most.
Part 2: Updates of Model-Based Definition

Model-Based Definition – GD&T and 3D Annotation
What is it? The demand for integration between design and manufacturing has grown and the need for more information from 3D models has become part of the design process. Based on this shift, Inventor 2018 added fully integrated Autodesk Model Based Definition (MBD). Now, a user can fully design and dimension a 3D model with tolerances and further reduce or eliminate 2D documentation entirely.
Why I’m excited. The manufacturing industry has started to push toward model-based engineering. Users can now leverage MBD data in things like 3D PDF as a way to get your model information to manufacturing while skipping the entire 2D drawing creation process. It may take a while for this to sink in… you can now use your 3D model as the deliverable. That’s remarkable. I know plenty of users who will save tons of hours in documentation by simply adding GD&T symbols and assembly notes within the 3D files themselves. Best of all, the tools are intelligent. Users no longer have to worry about which symbols to use for certain tolerances or geometric characteristics. Inventor understands the geometry you are selecting and places the correct symbol for the features you are annotating.
In my eyes, this particular release could be looked at as a game changer, and MBD is a huge part of that. Model-Based Definition changes the process in which you get your designs to manufacturing. GD&T has oftentimes been a huge pain and a time-suck in the 2D documentation process, but now it can simply become an extension of your modeling workflow.
See how MBD can add value to your current and future workflows:
Join KETIV Virtual Academy and never stop learning new features introduced to the tools you use most.
Part 3: Autodesk Inventor New Measurement Tools
What is it? For our last highlighted feature, we’re looking at the newly redesigned Autodesk Inventor Measure Tool. One of the most common tasks used in the design process is checking the size and position of parts using the Measure Tool. In 2018, you can now select part and component priority within the dialog box and even dock the box in numerous places in your workspace, including the Model Browser itself.
The process in which you measure is not much different than it was before, but now the dialog box includes much more information, including dual units if specified.
Why I’m excited. These improvements may not be as game-changing as something like MBD or backward compatibility (AnyCAD), but they are most certainly way-of-life enhancements. The Autodesk Inventor tool went from four different commands to a single toolset for all of your measurement needs.
Being able to dock the Measure dialog box to the browser is going to save tons of clicks without having to use up precious screen real estate. Lastly, the dual unit function is a welcome addition to designers who work in a mixed unit environment.
The updated measure tool was just one of the many improvements based on user feedback. See the measure tool in action along with the other user-requested features added to Inventor 2018.
Join the KETIV Virtual Academy and never stop learning what new features are introduced to your favorite tools.
Autodesk Inventor 2017

Part 1: Enhanced AnyCAD Reference Models
What is it? Autodesk has taken extra steps to improve the Reference Model feature of Inventor. This improvement updates the behavior of Inventor when working with CATIA, SolidWorks, NX and Pro-E/Creo files. Most impressively, a STEP model can be referenced within the Inventor assembly and when the STEP file is updated, Inventor accounts for the design change.

Why I’m excited. While this is not a new feature, the improvements to interoperability mean being able to do more with Inventor without having to break my workflow. Being able to work in a mixed CAD environment, where another user is using another software, and then to be able to get updated models based on my co-worker’s design changes is an amazing thing that will surely greatly improve my ability to bring my designs to production.
Take a look at this video for more information about this feature:

Part 2: Component Transparency
What is it? You can now toggle the transparency of a component in an assembly without applying an Appearance override.

Why I’m excited. This feature gets rid of the hassle of changing the appearance of components to work on other details of your assembly. This is opposed to current options like visibility, suppression, or appearance, which get the job done, but at a much more rudimentary level. This feature is much more intuitive and gives a great visual on the assembly you’re working with so you know exactly what you’re working on at all times.

Part 3: 3D PDF Publishing
What is it? Autodesk has finally integrated the capability to export 3D PDFs from Inventor. Users can now export their models in 3D PDF format to be viewed in Adobe Acrobat Reader. There are also options to create custom 3D PDF templates to change the arrangement of exported elements in the PDF.

Why I’m excited. This feature ties in with a post from a couple weeks ago, 3D PDF is a feature that has one of the most views and kudos on the IdeaStation and as such it’s a feature I know the entire community is excited about.
3D PDF is a file format that allows users to not only view model representations but to zoom, pan, and revolve models within the PDF. It’s a powerful viewing tool that requires no more than Adobe Acrobat Reader, which many people already have. This allows users to share files with whomever they please without worrying about file compatibility and eliminating the hassle of downloading proper CAD viewing software. This improves communication between all parties involved and allows for a better flow from design to approval to production.
Watch this video for more information and see the publishing process in action:

Full Windows 10 and High-Res (4K) Monitor Support
What is it? Autodesk has listened! With more users switching to the newest operating systems and monitor technology, software compatibility issues have plagued some users. Two of the most common issues were Windows 10 and high-resolution displays. There have been service packs for the most common applications, but no Inventor products were Windows 10 supported out-of-the-box until now with the 2017 releases. For users of high-res displays, there was a workaround, but it only fixed some of the icons, while others still remained too small to feasibly use.

Why I’m excited. The addition of these features means that people can comfortably move to newer operating systems with no worry about compatibility issues with the software. Users who are early adopters of high-res monitors can now see their projects with proper scaling, as opposed to having to reduce the resolution of the monitor, rendering its high-res capability useless. These features don’t necessarily change the workflow in Inventor, but they relieve any questions regarding software and hardware compatibility that were issues for users who are up-to-date with the newest technological advances.

Part 5: Connected Design
What Is It? Connect with collaborators and review feedback directly in Inventor. Design shares can also be created in Inventor and sent to A360.

Why I’m excited. Design reviews have always been a complex series of sending, receiving, and reviewing particular models and drawings. This process can become even more complex if collaborators are not in the same geographical area. Autodesk has made this process easier by keeping it all in one platform. No longer do people need to email countless models and drawings to one another and keep up with updates and feedback from numerous people.
Watch this video for more information and see how it all works.

Part 6: Presentation Environment
What is it? Inventor 2017 has implemented workflow improvements over older releases for creating presentations of exploded views, animations, assembly instructions, and drawings of your parts and assemblies.

Why I’m excited. Setting up views is easier than ever. Creating exploded views is as simple as pushing and pulling the components to your desired locations, while every move is tracked and recorded by the storyboard. Snapshots can be taken at any moment during the view creation process, at any desired camera angle.
Storyboards can be used to layout animations. All actions in the animation are included within the storyboards, which can then be converted to a video, or a raster image. Creating drawings from exploded views is now simpler in 2017. You can simply create drawing views just by clicking a particular snapshot and choosing the “Create Drawing View” option.
With these new changes, users can more easily share their designs and assemblies without having to send multiple CAD files or drawings.
Take a look at this video to see it in action:

Part 7: Tube and Pipe
What is it? The Tube and Pipe environment in Inventor 2017 received upgrades to make your life easier. The Find in Browser context menu option is now enabled during route creation and also when placing flexible hose fittings. Two new context menu options, Offset Point, and Intermediate Point, were added to allow you to create multiple intermediate points when you route a flexible hose with fittings. Also, the message box that displays when you check a problematic bend radius has been replaced with a new Show Violations dialog box.

Why I’m excited. This pass of Tube and Pipe enhancements is all working faster. With the new Offset Point and Intermediate Point options, you can set multiple intermediate points as you design your route, before placing the second fitting. The new Show Violations dialog box displays a tree view of spline segments where bend radius violations occur. Selecting a node in the dialog box highlights the corresponding segment in the graphics window, which helps you find the offending section quickly.
Watch this video to find out more:

Last week, Autodesk released the Inventor 2017 R2 update which includes productivity enhancements voted on by Inventor users worldwide. Over 40 enhancements have been made in sketching, part and assembly modeling, design automation, drawings, interoperability, and presentations to help you get your work done faster and make great products. Today, I’ll show you some of my favorites.
General:
WorkFlow Enhancements:
- Part/Assembly/Flat pattern sketches now maintain the properties specified in the Geometry Properties dialog box (for example, line type, scale, line color, and line weight) when exported as an AutoCADDWG file.
- You can elect to display or not display the mini-toolbars when you access one of the following commands: Extrude, Revolve, Fillet, Shell, Face Draft, Chamfer, and Joint. These dialog boxes have a mini-toolbar that displays alongside of the dialog box. The available options on these mini-toolbars are the same as the dialog box options.
- To maximize the amount of graphical space, use the new View panel > User Interface panel > Mini-Toolbar command to turn off the display of these mini-toolbars.
- You can now easily jump back and forth to a different point in time. Your undo/redo history now displays in the new Undo/Redo drop-down menus. Click a drop-down arrow and select from a list of actions you want to undue or redo.
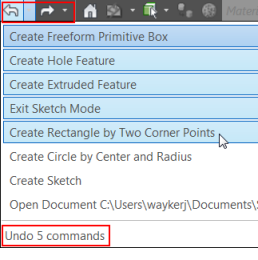
- Some of these changes you’re seeing here were actually thought up by users like you and implemented by the Autodesk Product Development team. So If you have ideas as to how to improve the program we want to hear !! You can post your ideas to the Autodesk Inventor Ideastation page and who knows you might just see your implemented in a future update. For the link click here.
Parts:
Automate Selection of all Faces or Edges Tangent to the Pre-Selected Faces or Edges:
You can now quickly create a selection set of all the faces or edges tangent to each other. In the graphics window:
-
- With the left mouse button, double-click a face or an edge.
OR
- Select one or more faces or one or more edges, right-click, and select Select Tangencies from the context menu.
Note: Hold down the CTRL key to select more than one face or edge.
Example selecting tangent faces: Right-click a face, select Select Tangencies OR with the left mouse button, double-click a face. Result: All tangent faces are selected.
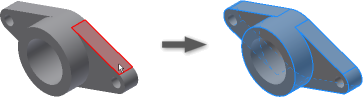
Examples of uses
- Use the selection set of tangent faces to:
- Delete the selection set with Delete Faces.
- Assign an appearance to the selection set.
- Add or remove thickness to faces, or create an offset surface from a part face with the Thicken/Offset command.
- Use the selection set of tangent edges to:
- Fillet or chamfer the preselected edges.
- Review or check for tangency conditions or closed loops.
Enhancements to Revision Tables and Parts Lists Exported Excel Formats:
- You can now select an excel template file (.xlsm) with macros when exporting. Macros are maintained in the exported excel file.
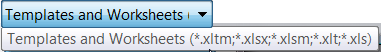
For more information on selecting an excel template for export see, Microsoft Excel Export Options Reference
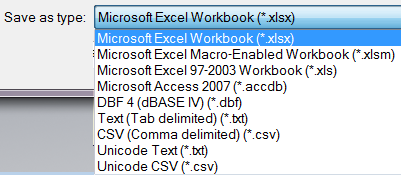
- You can now export Revision Tables and Parts Lists to an excel macro-enabled file (.xlsm). The following excel file types are now supported from a Parts List or Revision table for export: *.xltm;*.xlsx;*.xlsm;*.xlt;*.xls excel templates.
Drawings:
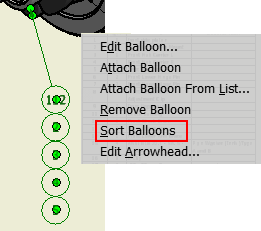
Reorder Attached Balloons with the New Sort Balloons Context Menu Option (not available in Inventor LT):
You can now reorder the attached balloons by their value. First, attach balloons using the Attach Balloon From List context menu option. Then, after closing the Attach Balloon dialog box, right-click on the balloon stack and select Sort Balloons. Values are automatically reordered.
- Numeric-attached balloons are reordered from smallest to largest.
- Alpha attached balloons are reordered from A to Z.
If you are interested in learning more about these changes, be sure to visit the Autodesk page for yourself where you’ll get a complete rundown of all the changes implemented.
View our instructional blog post for a step-by-step process for Downloading the Inventor 2017 R2 Update.
Have an idea for a feature? Check out the Inventor IdeaStation page where you can share your ideas about how to improve Inventor with the Development Team.

What’s New in Autodesk Inventor 2017 continues to deliver an exceptional modeling experience. There are hundreds – if not thousands – of suggestions that Autodesk gets from customers throughout each release. Instead of waiting until the yearly release, Autodesk implements some of these enhancements and changes midway through a release cycle.
In the past, updates have included tools such as Shape Generator and Connected Design with A360. The newest release, Inventor 2017.3, is no exception.
Let’s take a look at some of the newest enhancements and updates.
Want to see what’s new in Inventor 2018? Read our coverage here.
Enhanced Measure Commands
You can now restart the measure command by clicking anywhere within the window. This allows you to more easily perform multiple measurements in a row. Dual units are also available, allowing you better measure distances, loops, and area.

Multiple Profile Selection (Cross-Window)
Select multiple closed profiles in a single click when creating certain features. You’ll never have to zoom in to select those tiny profiles again!

Project Geometry Improvements
Select Tangencies is now available within the What’s New in Inventor 2017. It is Project Geometry command. Grab entire edges with fewer clicks. A major improvement has to deal with projected sketch references. The references are maintained even after you redefine your sketch. The associativity is maintained for projected geometry, loops, and even cross-part references.

Text to Geometry
You can now edit sketch text to sketch geometry, to create text engravings for laser etching.

Improvements to Interference Analysis
You can now treat subassemblies as a single component, and even ignore any interference within subassemblies if desired. New tooltips have been added to more easily determine your interference types.

3D PDF Enhancements
3D PDF creation has sped up drastically, and now supports view representation color overrides.

Tutorial Creation
Last but not least is the Tutorial Creator. You can create your own tutorials to share with colleagues or publicly with the Inventor user base.

